An all-in-one platform for cyber-physical resilience assessment
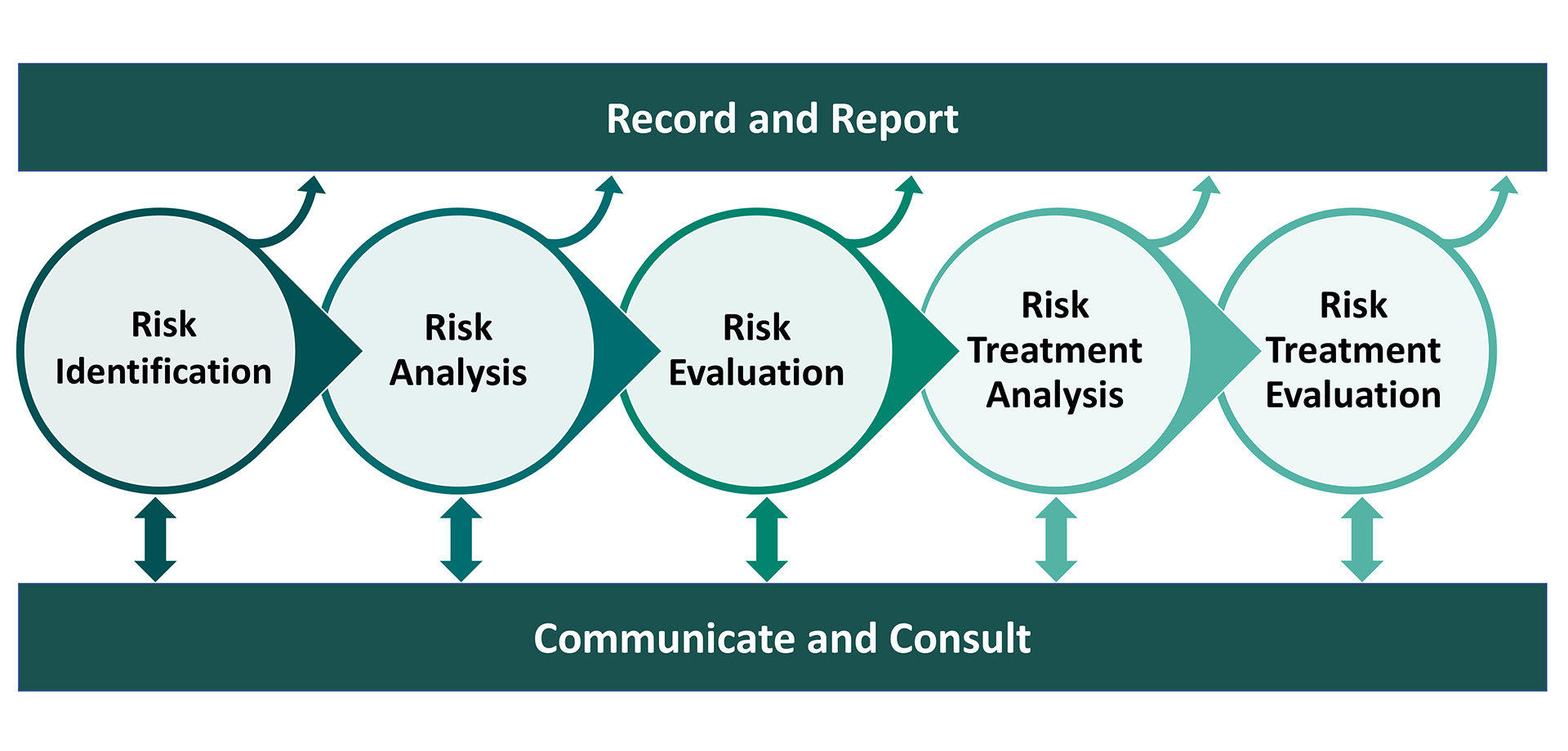
The PROCRUSTES Testbed is a unique all-in-one platform for urban water utilities to assess their preparedness and their system’s resilience under a wide range of cyber and physical threats. PROCRUSTES facilitates a complete workflow for combined cyber-physical risk assessment, in line with the latest CER and NIS2 Directives, and adhering to the ISO 3100:2018 risk management principles and guidelines. It helps utilities to a) identify threats, b) analyse c) evaluate them through uncertainty-aware scenarios and d) to explore and evaluate effectiveness of operational and technical mitigation options to manage these risks.
PROCRUSTES provides advanced decision support and analysis tools, supports multiple workflows according to the end goal of analysis and protects sensitive data through its role-based access control (RBAC). Key novelties include: socio-technical analysis of any utility’s threat landscape via agent-based models, water-quality (WQ) capable CP stress-testing engine, CP attack aware WQ sensor placement tools, uncertainty-aware scenario formulation and analysis, computationally efficient parallel processing of scenarios, threat-relevant measures suggestions with cost-benefit analysis, and interactive result visualizations for risk communication.
This tool is the continuation of the RAET platform, developed and showcased in real-world system under the STOP-IT project, further enhanced under the funding of the Hellenic Foundation of Research and Innovation (GA: HFRI-FM17-2918, https://procrustes.gr/en/) and with the support of the Greek water sector. In both stages, the feedback received from water utilities helped ensure that the platform operates as expected and supports the objectives for a diverse set of water utilities.
This tool is the continuation of the RAET platform, developed and showcased in real-world system under the STOP-IT project, further enhanced under the funding of the Hellenic Foundation of Research and Innovation (GA: HFRI-FM17-2918, https://procrustes.gr/en/) and with the support of the Greek water sector. In both stages, the feedback received from water utilities helped ensure that the platform operates as expected and supports the objectives for a diverse set of water utilities.
Key components and functionalities of PROCRUSTES
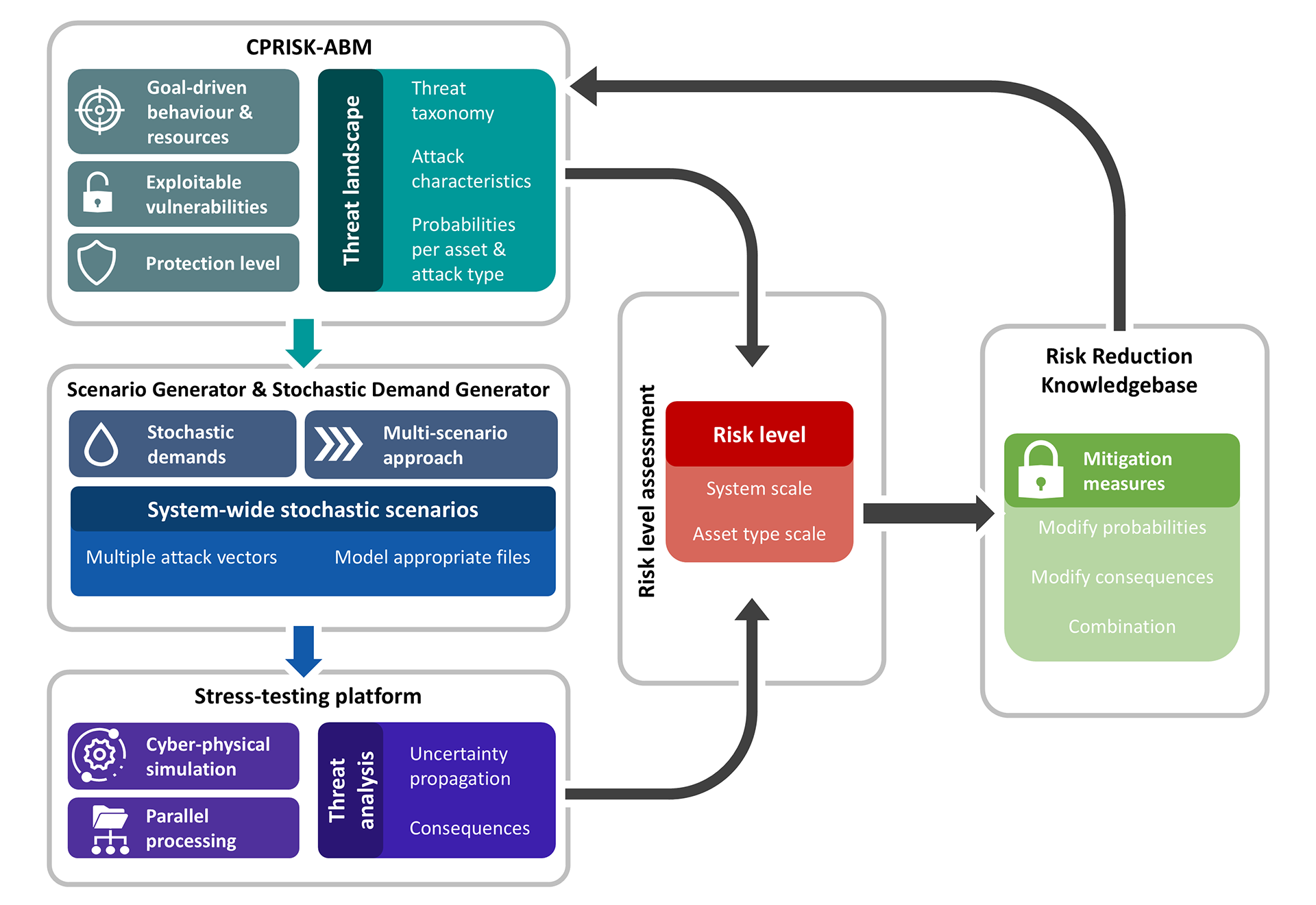
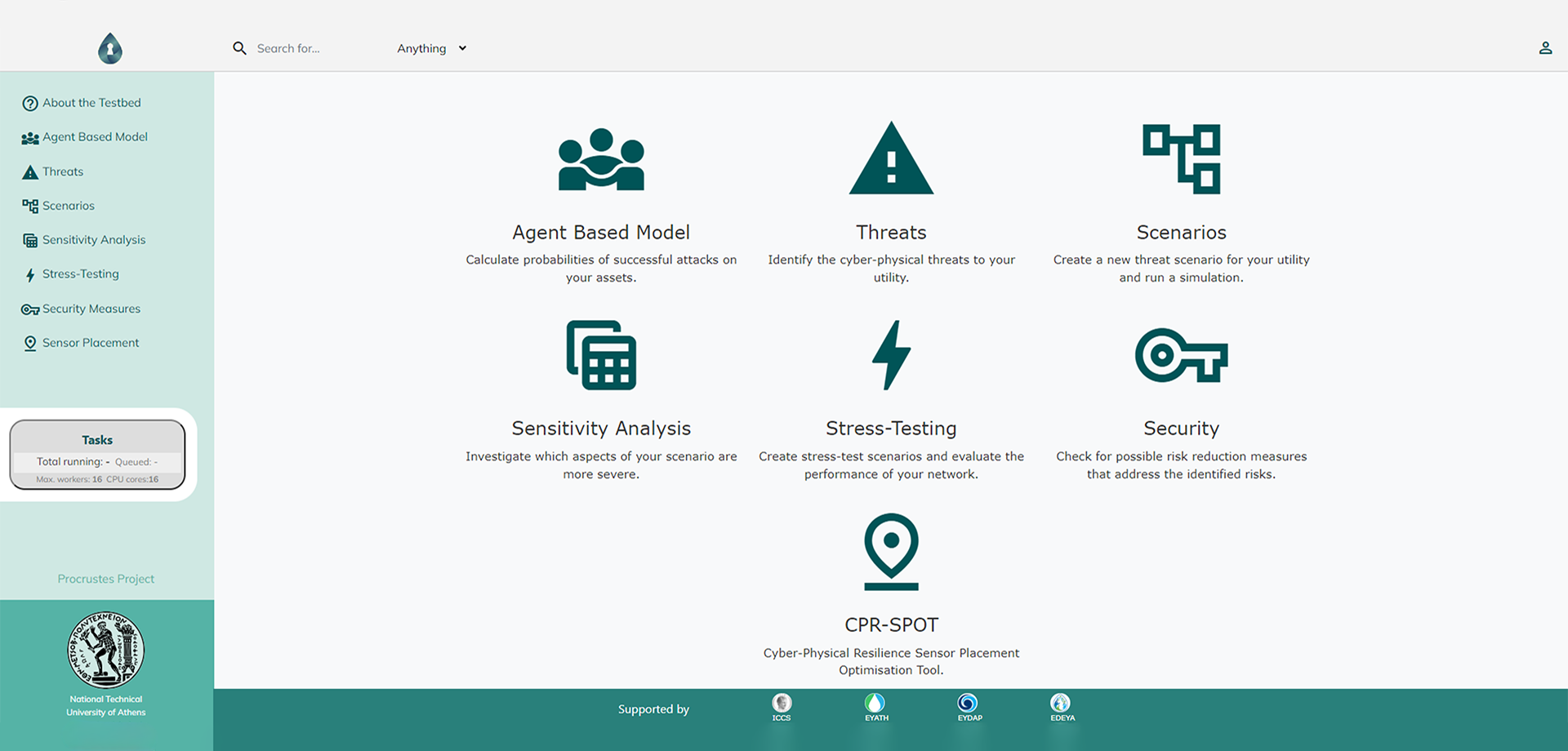
Designed as a modular platform, PROCRUSTES integrates state-of-the-art tools designed to support users across every stage of the risk analysis framework. The platform also adapts to the objectives and end goals of its users, offering multiple levels of interactions, that (a) allow the investigation of either single scenarios or multiple scenarios and (b) facilitate both comprehensive, system-wide assessments and threat specific risk assessments.
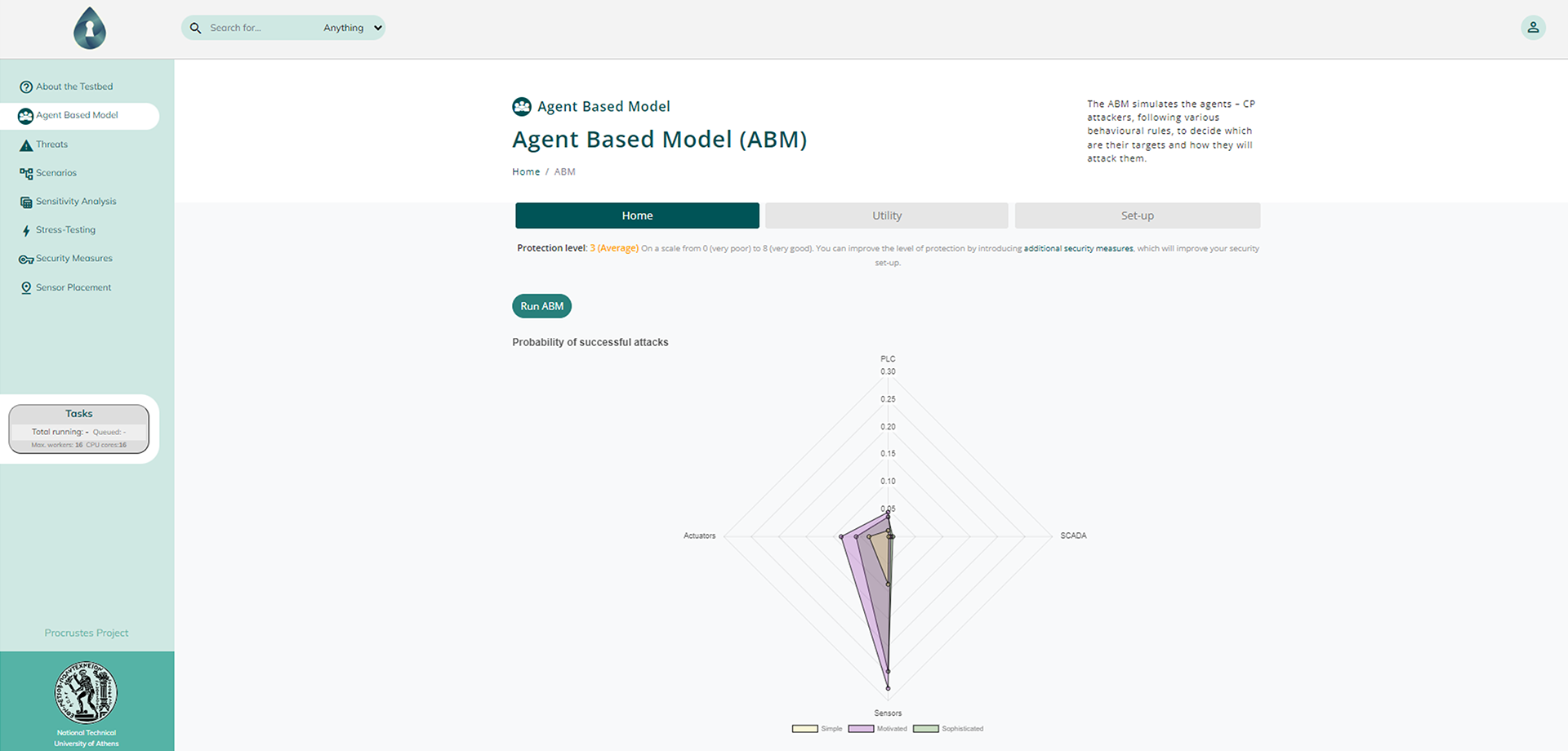
Utilities can employ an Agent-Based Modelling approach (CPRISK-ABM) to explore the effects that different cyber-security practices and system design traits have over the utility’s threat landscape and derive probabilities of attacks against assets of their system. The derived threat landscape can be further explored in terms of quantitative consequences via the intuitive Scenario Generator, capable of preparing, simulating, and managing scenarios. Based on their end-goal, users can select between different analysis modes that include:
a) single scenario to explore event-specific consequences,
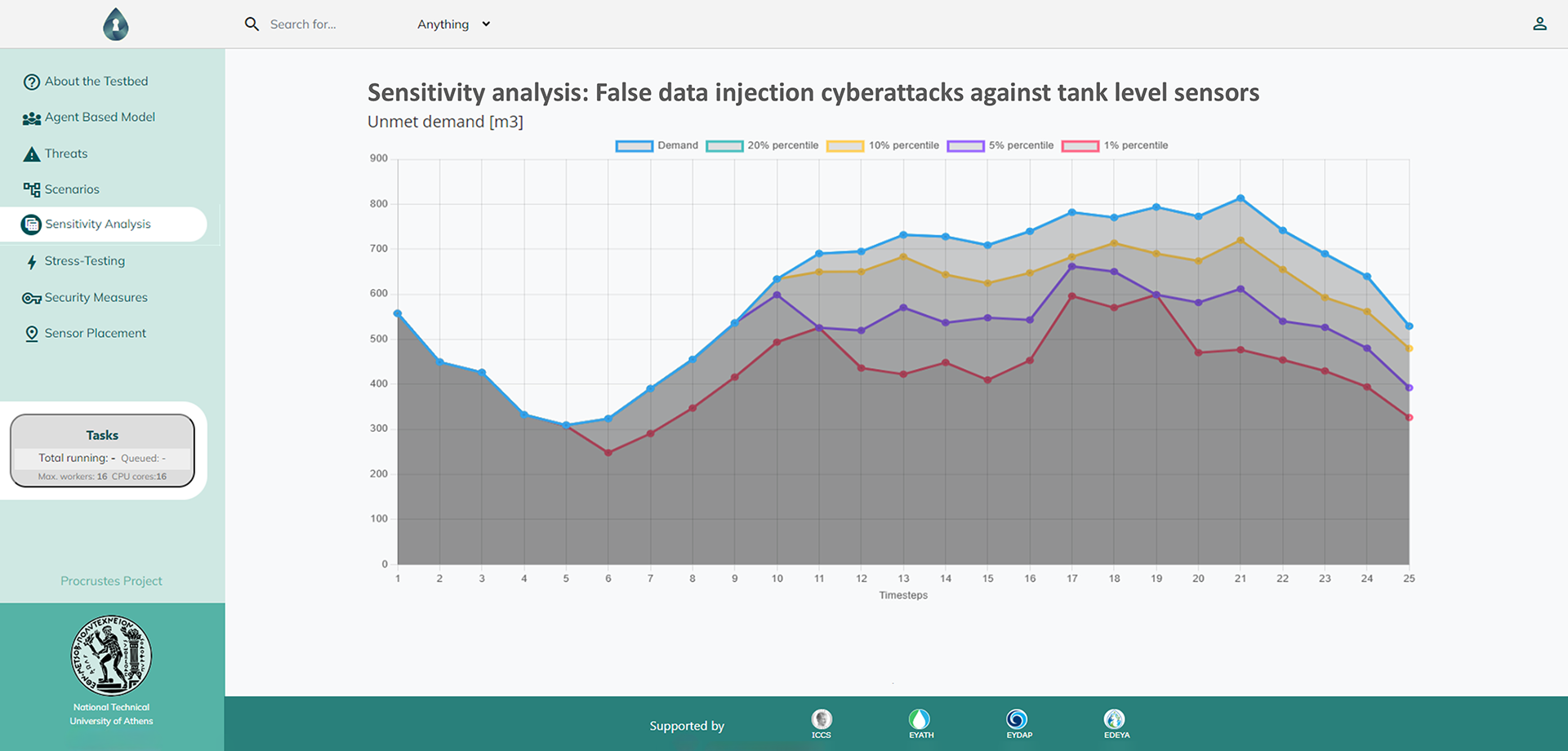
b) sensitivity analysis to identify critical assets of the system,
c) system-wide stress-testing based on the ABM results to define the risk level of the utility,
d) selection and evaluation of risk treatment measures for evidence-based decision making.
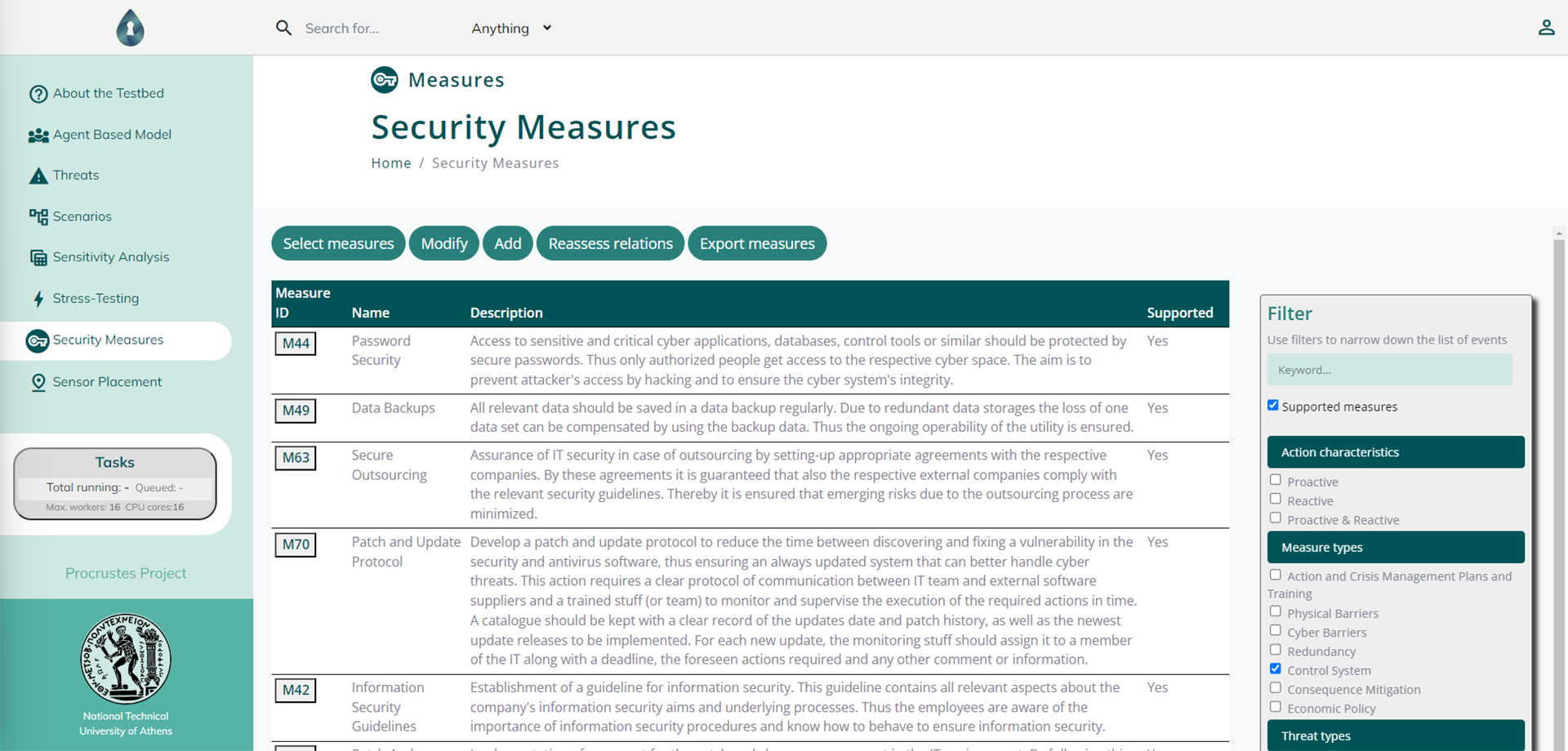
The later analysis is achieved by directly incorporating and parameterising potential measures recorded in the integrated Risk Reduction Knowledge Base (RRKB). In all modes, users can pair the analysis with stochastically generated demands using the integrated Stochastic Demand Generator and thus be presented with quantitative insights that account for uncertainties. All the PROCRUSTES scenario analysis procedures are driven by the RISKNOUGHT cyber-physical stress-testing tool, coupled with a sophisticated parallelisation process which allows users to run large batches of simulations in a substantially reduced time. The scenario results are presented to users in multiple levels of details, each serving a different scope of decision support, and span from individual key performance indicators (e.g., total unmet demand, spatial extent of contamination etc.), to timeseries and map-like features, up to the aggregation of the total risk level in risk matrices at system and asset level.
Within the platform, users can also explore new water quality sensor placement strategies by employing the Cyber-physical Resilience Sensor Placement Optimisation Tool (CPR-SPOT) and select between creating a new quality sensor layout or upgrade the existing with a user-defined number of additional sensors.
a) single scenario to explore event-specific consequences,
b) sensitivity analysis to identify critical assets of the system,
c) system-wide stress-testing based on the ABM results to define the risk level of the utility,
d) selection and evaluation of risk treatment measures for evidence-based decision making.
The later analysis is achieved by directly incorporating and parameterising potential measures recorded in the integrated Risk Reduction Knowledge Base (RRKB). In all modes, users can pair the analysis with stochastically generated demands using the integrated Stochastic Demand Generator and thus be presented with quantitative insights that account for uncertainties. All the PROCRUSTES scenario analysis procedures are driven by the RISKNOUGHT cyber-physical stress-testing tool, coupled with a sophisticated parallelisation process which allows users to run large batches of simulations in a substantially reduced time. The scenario results are presented to users in multiple levels of details, each serving a different scope of decision support, and span from individual key performance indicators (e.g., total unmet demand, spatial extent of contamination etc.), to timeseries and map-like features, up to the aggregation of the total risk level in risk matrices at system and asset level.
Within the platform, users can also explore new water quality sensor placement strategies by employing the Cyber-physical Resilience Sensor Placement Optimisation Tool (CPR-SPOT) and select between creating a new quality sensor layout or upgrade the existing with a user-defined number of additional sensors.
Multiple-users provision
Cooperative platform
Different user profiles
Single-view across devices
Parallelization
Multi-processing scenarios
Multi-tasking
Enhanced User Experience
Internet or Intranet access
Interdepartmental workflow
Tiered user access with role-based access and permissions
Secure handling of sensitive data
Modular Architecture
Customizable
Scalable
Upgradeable
For more details and use cases of the PROCRUSTES Testbed see here.
RELEVANT PUBLICATIONS
- Moraitis, G.; Sakki, G.-K.; Karavokiros, G.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Tsoukalas, I.; Kossieris, P.; Makropoulos, C. Exploring the Cyber-Physical Threat Landscape of Water Systems: A Socio-Technical Modelling Approach. Water 2023, 15, 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091687
- Moraitis, G.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Koutiva, I.; Tsoukalas, I.; Karavokiros, G.; and Makropoulos, C. The PROCRUSTES testbed: tackling cyber-physical risk for water systems, EGU General Assembly 2021, online, 19–30 Apr 2021, EGU21-14903, 2021, https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-egu21-14903
- Nikolopoulos, D., Moraitis, G., Makropoulos, C., 2021. 7. Strategic and Tactical Cyber-Physical Security for Critical Water Infrastructures, in: Soldatos, J., Praça, I., Jovanovic, A. (Eds.), Cyber-Physical Threat Intelligence for Critical Infrastructures Security: Securing Critical Infrastructures in Air Transport, Water, Gas, Healthcare, Finance and Industry. Now Publishers, pp. 159–187. https://doi.org/10.1561/9781680838237.ch7
- Moraitis, G.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Bouziotas, D.; Lykou, A.; Karavokiros, G.; Makropoulos, C. Quantifying Failure for Critical Water Infrastructures under Cyber-Physical Threats. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020108, https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001765
- Koutiva, I.; Moraitis, G.; Makropoulos, C. An Agent-Based Modelling approach to assess risk in Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS). In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology; Athens, Greece, 2021, https://doi.org/10.30955/gnc2021.00194
- Nikolopoulos, D.; Moraitis, G.; Bouziotas, D.; Lykou, A.; Karavokiros, G.; Makropoulos, C. Cyber-Physical Stress-Testing Platform for Water Distribution Networks. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020061, https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0001722
- Moraitis, G.; Tsoukalas, I.; Kossieris, P.; Nikolopoulos, D.; Karavokiros, G.; Kalogeras, D.; Makropoulos, C. Assessing Cyber-Physical Threats under Water Demand Uncertainty. In Proceedings of the EWaS5; MDPI: Basel Switzerland, 2022; p. 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021018
- Nikolopoulos, D.; Moraitis, G.; Karavokiros, G.; Bouziotas, D.; Makropoulos, C. Stress-Testing Alternative Water Quality Sensor Designs under Cyber-Physical Attack Scenarios. In Proceedings of the EWaS5; MDPI: Basel Switzerland, 2022; p. 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2022021017
- Nikolopoulos, D.; Makropoulos, C. Stress-testing water distribution networks for cyber-physical attacks on water quality. Urban Water J. 2021, 00, 1–15, https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2021.1995446